Subtotal $0.00
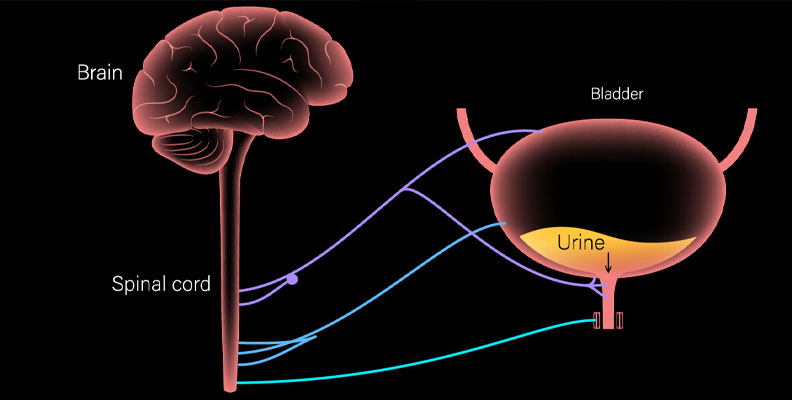
Neurogenic bladder is a condition where bladder function is impaired due to nerve damage, often caused by spinal cord injuries or chronic neurological disorders such as multiple sclerosis or stroke. It can result in urinary retention, incontinence, and recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs) if left untreated.
Common Symptoms:
- Difficulty emptying the bladder completely.
- Frequent urination or urgency.
- Urinary incontinence (loss of bladder control)
- Recurrent UTIs
Awareness of neurogenic bladder is not only about recognizing the symptoms but also about the importance of early diagnosis and proper treatment to prevent serious complications such as kidney damage and recurrent urinary infections. Choosing the right treatment plan—whether behavioral therapy, medications, or neuromodulation devices—can significantly improve quality of life and provide long-term control and prevention.
Diagnosis:
Doctors use:
- Urodynamic testing (bladder function test).
- Urine analysis to detect infection
- Imaging (ultrasound, MRI, or CT scans)


Treatment Options:
- Early diagnosis prevents kidney damage and infections
- Behavioral therapy and bladder training improve urinary control
- Medications (antimuscarinics) reduce bladder overactivity
- Neuromodulation devices (InterStim) for severe cases
Prevention and Awareness:
Recognizing the symptoms of neurogenic bladder early enables patients to seek medical care, protecting kidney health and reducing complications.




Comments are closed